In today’s fast‑paced digital environment, ensuring that your applications can handle high volumes of traffic is critical. Load testing—load testing—simulates real‑world user activity to verify that systems remain responsive and reliable even under stress. Recent trends indicate that over 70% of enterprises are boosting their investments in performance validation, with a 20% surge in the adoption of website speed test and page speed monitoring solutions. This article explores the top enterprise load testing tools for 2025, from open‑source platforms to premium solutions that deliver advanced API monitoring and real‑time insights.
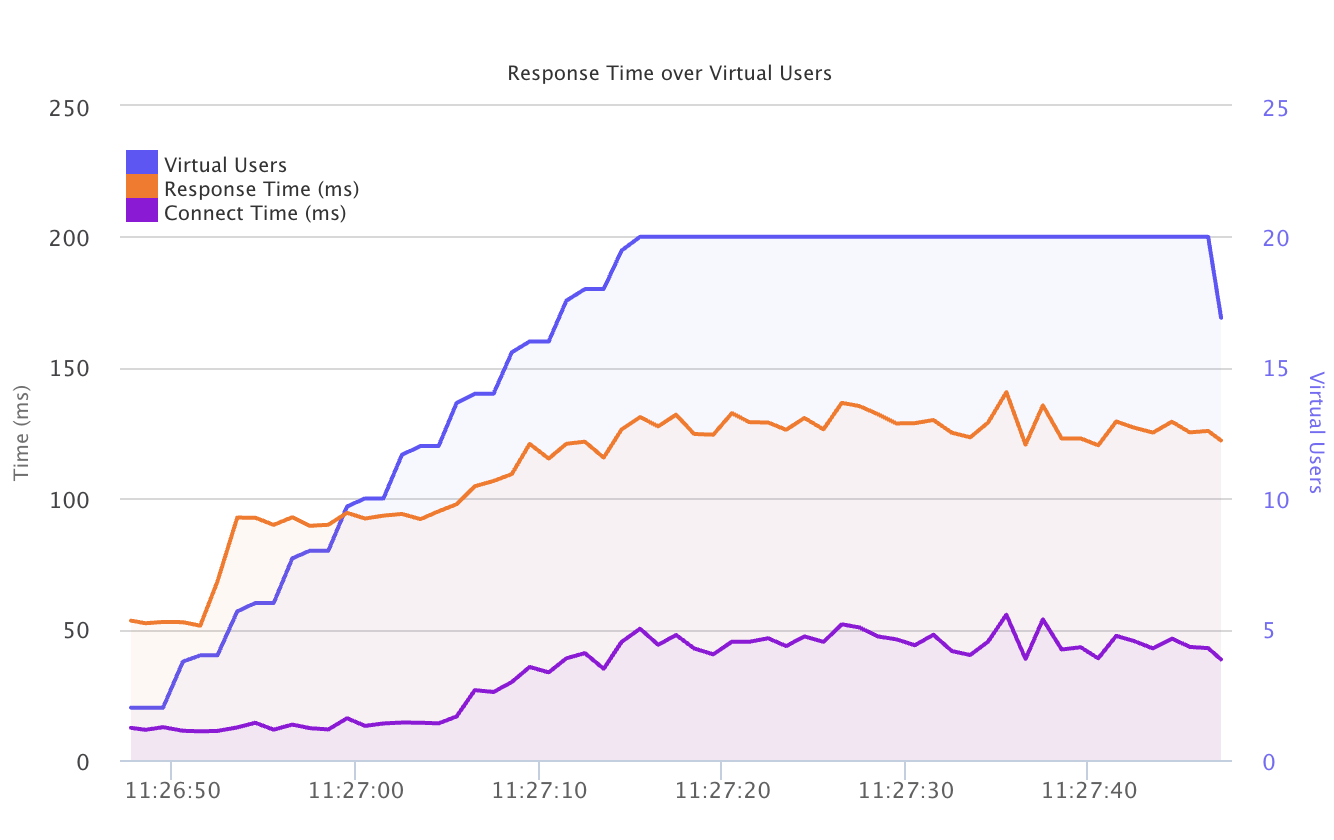
Comparative Summary of Enterprise Load Testing Tools
| Tool | Best For | Key Features | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| LoadFocus | Modern, intuitive cloud‑based testing | Offers real‑time analytics, automated testing, and a user‑friendly dashboard for agile performance insights. | Agile load testing with advanced reporting features |
| Apache JMeter | Open‑Source flexibility and scalability | Extensive plugins, robust community support, customizable test plans, and integration with CI/CD pipelines. | Testing web and application performance |
| Micro Focus LoadRunner | Enterprise‑grade performance testing | Advanced scripting, detailed reporting, and integrated performance monitoring that scales for large‑scale enterprise applications. | Mission‑critical, high‑traffic environments |
| Gatling (FrontLine) | Continuous testing with real‑time insights | High‑performance engine, real‑time metrics, seamless CI/CD integration, and enhanced reporting via its enterprise edition (FrontLine). | Continuous integration and automated testing |
| BlazeMeter | Cloud‑based load testing and API performance | Scalable cloud execution, comprehensive analytics, and robust reporting tools for distributed load simulations. | API testing and global load simulations |
Top 5 Enterprise Load Testing Tools to Try in 2025
1. LoadFocus
Category: Modern, Intuitive Cloud‑Based Testing
Is Your Infrastructure Ready for Global Traffic Spikes?
Unexpected load surges can disrupt your services. With LoadFocus’s cutting-edge Load Testing solutions, simulate real-world traffic from multiple global locations in a single test. Our advanced engine dynamically upscales and downscales virtual users in real time, delivering comprehensive reports that empower you to identify and resolve performance bottlenecks before they affect your users.
Overview:
LoadFocus is a contemporary load testing tool offering a sleek online interface and powerful cloud‑based performance analysis. It combines real‑time analytics with automated testing to deliver immediate, actionable insights. Its user‑friendly dashboard and flexible pricing make it an excellent choice for agile enterprises. Additionally, explore our baseline comparison feature for performance benchmarking.
Key Features:
- Rapid, cloud‑based test deployment
- Detailed, real‑time analytics and reporting
- Automated scheduling and execution of tests
- Intuitive, interactive user interface
Pros:
Think your website can handle a traffic spike?
Fair enough, but why leave it to chance? Uncover your website’s true limits with LoadFocus’s cloud-based Load Testing for Web Apps, Websites, and APIs. Avoid the risk of costly downtimes and missed opportunities—find out before your users do!
- Quick setup and fast, actionable insights
- Cost‑effective with flexible pricing plans
- Tailored for agile development and rapid iterations
Cons:
- May have limitations for extremely complex test scenarios
- Relatively new compared to some established legacy tools
Use Case:
Best for enterprises needing a swift, modern approach to load testing that delivers advanced analytics and automation.
Pricing:
Flexible pricing plans with a free trial option. For more details on pricing, visit our pricing page.
2. Apache JMeter
Category: Open‑Source and Flexible Testing
LoadFocus is an all-in-one Cloud Testing Platform for Websites and APIs for Load Testing, Apache JMeter Load Testing, Page Speed Monitoring and API Monitoring!
Overview:
Apache JMeter is a well‑established open‑source tool that enables organizations to simulate heavy loads on servers, networks, or applications. Its extensive plugins and customizable test plans make it ideal for enterprises seeking flexibility and cost‑efficiency. For more tailored guidance, explore our dedicated JMeter load testing resource.
Key Features:
- Robust community support and regular updates
- Extensive plugin ecosystem
- Ability to test a variety of applications and protocols
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines
Pros:
- Free and open‑source
- Highly customizable
- Wide adoption and extensive community resources
Cons:
- Steeper learning curve for non‑technical users
- Limited out‑of‑the‑box reporting compared to commercial tools
Use Case:
Ideal for organizations that require a versatile, budget‑friendly solution for performance testing.
Pricing:
Free and open‑source.
3. Micro Focus LoadRunner
Category: Enterprise‑Grade Load Testing
Overview:
Micro Focus LoadRunner is a premium solution engineered for large enterprises. It features advanced scripting capabilities, comprehensive reporting, and integrated performance monitoring to ensure applications remain robust under heavy loads. Enhance your performance insights with our proven page speed monitoring strategies.
Key Features:
- Advanced scripting and protocol support
- Comprehensive reporting and analysis
- Integration with multiple development tools
- Detailed analytics to pinpoint performance bottlenecks
Pros:
- Industry‑leading with robust feature sets
- Scalable for high‑volume, complex test scenarios
- Strong vendor support and continuous updates
Cons:
- High cost relative to open‑source alternatives
- Complexity in setup and configuration
Use Case:
Best suited for enterprises managing complex, high‑traffic applications needing detailed performance insights.
Pricing:
Commercial licensing with enterprise pricing.
4. Gatling (Enterprise Edition: Gatling FrontLine)
Category: Continuous Testing & Real‑Time Reporting
Overview:
Gatling is renowned for its high‑performance engine and real‑time analytics, making it a favorite in DevOps environments. The enterprise edition, Gatling FrontLine, adds features for continuous integration and automated testing, ensuring that performance issues are caught early. Check out our load testing reports for deeper insights into test results.
Key Features:
- High‑performance, scalable testing engine
- Real‑time metrics and analytics
- Seamless integration with CI/CD pipelines
- Detailed reporting and continuous feedback
Pros:
- Optimized for continuous testing environments
- Clear, actionable real‑time insights
- Scalable for high‑volume tests
Cons:
- Enterprise edition requires a premium investment
- May need additional configuration for complex setups
Use Case:
Ideal for organizations focused on continuous delivery that need immediate, real‑time performance data.
Pricing:
Offers both an open‑source version and an enterprise edition (FrontLine) with commercial licensing.
5. BlazeMeter
Category: Cloud‑Based Load Testing and API Performance
Overview:
BlazeMeter delivers a cloud‑based platform for executing load tests that simulate thousands of virtual users. Its user‑friendly interface and robust integrations make it an excellent option for testing web, mobile, and API performance across distributed environments. For additional context, refer to our free load test option.
Key Features:
- Scalable, cloud‑based execution
- Supports comprehensive API, mobile, and web testing
- Customizable, detailed reporting
- Seamless integration with modern CI/CD frameworks
Pros:
- Eliminates infrastructure overhead via cloud execution
- Intuitive setup and usage
- In-depth analytics and reporting capabilities
Cons:
- Dependent on stable internet connectivity
- Costs can rise with extremely high usage volumes
Use Case:
Ideal for organizations seeking flexible, scalable load testing solutions with robust cloud support.
Pricing:
Subscription‑based with a free trial available.
FAQs
What is Load Testing?
Load testing is the process of simulating multiple users accessing a system concurrently to assess its performance under stress. This testing helps identify bottlenecks, ensuring that applications remain stable and responsive during peak traffic periods.
Why Do We Need Load Testing?
Load testing is essential to ensure that applications can handle real‑world usage without performance degradation. It prevents downtime, enhances user experience, and ensures that infrastructure scales efficiently. By leveraging tools with advanced load testing reports, organizations can detect and address issues before they impact end users.
Tips to Choose the Best Load Testing Tools
- Assess Your Requirements: Determine whether you need a free, open‑source solution like Apache JMeter or a premium tool like Micro Focus LoadRunner.
- Scalability: Ensure the tool can simulate the required load and manage your application’s traffic.
- Integration: Opt for tools that integrate smoothly with your CI/CD pipelines and other development processes.
- Reporting & Analytics: Prioritize solutions that offer detailed load testing extensions and real‑time insights.
- Ease of Use: A user‑friendly dashboard can streamline testing and reduce the learning curve.
What is enterprise testing?
Enterprise testing is a structured approach to validating all software components, integrations, and data flows across an organization. It encompasses functional checks, performance and load assessments, security validations, and compliance verifications—ensuring that each application or system not only works on its own but also interacts correctly with other enterprise services and meets corporate policies.
How to test an enterprise application?
- Test Strategy & Planning: Define scope (functional, performance, security), identify stakeholders, select tools, and set entry/exit criteria.
- Environment & Data Setup: Mirror production configurations—servers, networks, middleware—and seed realistic test data to simulate real user behavior.
- Functional & Integration Testing: Verify individual modules and their interactions via unit, API, and end‑to‑end workflows.
- Non‑Functional Testing: Run load, stress, and scalability tests to measure responsiveness under peak usage; conduct penetration scans for security and usability reviews for user experience.
- Automation & Regression: Build automated suites in CI/CD pipelines to catch regressions quickly and maintain test coverage as the application evolves.
- UAT & Sign‑off: Facilitate business‑user testing of key scenarios, log defects, and obtain formal approval before deployment.
How is ERP testing done?
ERP testing follows the typical enterprise testing lifecycle but focuses on resource‑planning modules:
- Module Validation: Test each functional area (finance, procurement, HR) in isolation.
- Process Flow Testing: Execute cross‑module workflows like order‑to‑cash or procure‑to‑pay end‑to‑end.
- Data Migration & Reconciliation: Validate accuracy, completeness, and integrity of data moved from legacy systems.
- Performance & Volume Testing: Simulate hundreds or thousands of concurrent users and transactions.
- Security & Role‑Based Access Controls: Ensure permissions align with organizational policies and segregate duties appropriately.
- Regression & Go‑Live Dress Rehearsals: Re‑run critical scenarios after customizations or upgrades, and perform cutover simulations prior to production.
What does an enterprise test server do?
An enterprise test server provides an isolated, production‑like environment for:
- Deploying New Builds: Safely installing and configuring the latest code without affecting live systems.
- Automated Test Execution: Integrating with CI/CD tools to run unit, integration, and performance tests on every commit.
- Performance Monitoring: Capturing metrics (CPU, memory, response times) under controlled loads to detect bottlenecks.
- Environment Versioning: Maintaining multiple snapshots (QA, staging, sandbox) to parallelize testing activities and support troubleshooting.
What is an enterprise assessment?
An enterprise assessment is a holistic audit of an organization’s IT and business landscape. It typically covers:
- Process Maturity: Measuring practices against frameworks like ITIL, COBIT, or CMMI.
- Technology Health: Reviewing architecture, infrastructure, and application portfolios for scalability, security, and maintainability.
- People & Skills: Evaluating team competencies, organizational structure, and governance models.
- Risk & Compliance: Identifying regulatory gaps, security vulnerabilities, and operational risks.
The outcome is a gap analysis, prioritized recommendations, and a roadmap for improvement.
What is an enterprise KPI?
An enterprise Key Performance Indicator is a quantifiable metric tied to strategic objectives, used to gauge organizational success. Good KPIs are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time‑bound). Examples include:
- Revenue Growth Rate: Percent increase in sales over a period.
- Customer Retention Rate: Percentage of customers who continue using services year over year.
- System Uptime: Proportion of time critical applications remain available.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Net profit divided by total investment in projects or initiatives.
What is enterprise scan?
An enterprise scan is an automated vulnerability sweep across an organization’s infrastructure and applications. It uses specialized tools to:
- Discover Assets: Enumerate servers, endpoints, containers, and cloud services.
- Detect Vulnerabilities: Check for missing patches, insecure configurations, open ports, and known software flaws.
- Report & Prioritize: Generate risk‑ranked findings to guide remediation efforts and track compliance over time.
What is enterprise evaluation?
Enterprise evaluation is the ongoing review of projects, processes, or assets against predefined goals and benchmarks. It involves:
- Performance Measurement: Collecting data on key metrics and comparing them to targets.
- Benchmarking: Assessing practices or outcomes against industry standards or peer organizations.
- Stakeholder Feedback: Conducting interviews or surveys to gauge satisfaction and identify pain points.
- Action Planning: Translating findings into prioritized initiatives, tracking progress, and iterating to drive continuous improvement.


![9 Best IT Incident Management Software [2025] 9 Best IT Incident Management Software [2025]](https://loadfocus.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2024/08/it-management-tools.jpg)


